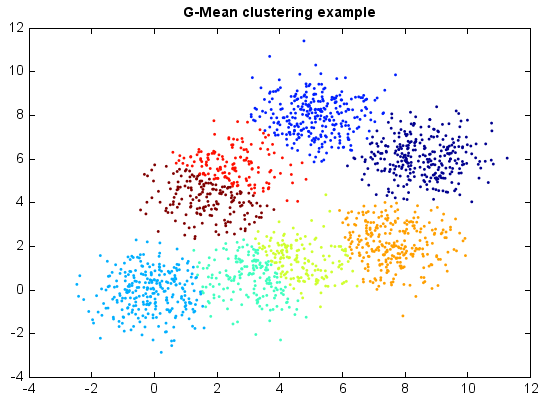
G-Means¶
G-Means clustering algorithm is another extended K-Means which tries to automatically determine the number of clusters by normality test. The G-Means algorithm is based on a statistical test for the hypothesis that a subset of data follows a Gaussian distribution. G-Means runs K-Means with increasing k in a hierarchical fashion until the test accepts the hypothesis that the data assigned to each K-Means center are Gaussian.
from miml import datasets
from miml.cluster import GMeans
from miml.utils import smile_util
fn = os.path.join(datasets.get_data_home(), 'clustering', 'gaussian',
'six.txt')
df = DataFrame.read_table(fn, header=None, names=['x1','x2'],
format='%2f')
x = df.values
model = GMeans()
y = model.fit_predict(x)
scatter(x[:,0], x[:,1], c=y, edgecolor=None, s=3)
title('G-Mean clustering example')